This document explains how to use the active or passive mode to connect to a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
In cPanel & WHM version 60 and later, the system enables passive ports 49152 through 65534 for Pure-FTPd servers and ProFTPD servers by default. If you use the CSF firewall plugin, the system also adds passive port ranges to your server’s firewall by default.
If you use the nftables, firewalld, or iptables applications for your firewall, you must enable firewall settings for the passive ports manually. For more information about firewalls, read our How to Configure Your Firewall for cPanel & WHM Services documentation.
FTP uses a data port and a command port to transfer information between a client and a server. During a typical active mode session, the command port uses port 21 and the data port uses port 20. When you use a passive mode session, however, the data port does not always use port 20.
In active mode, the FTP server responds to the connection attempt and returns a connection request from a different port to the FTP client. Network Address Translation (NAT) configurations block this connection request.
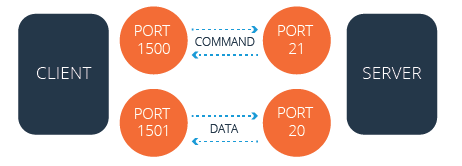
Active FTP
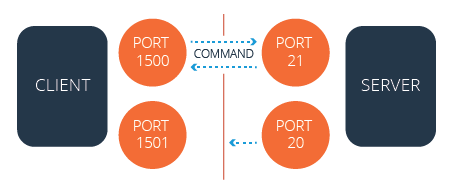
Active FTP (with firewall)
The firewall blocks the server’s attempt to communicate with the client because the server uses a different port than the first connection.
In passive mode, the FTP client initiates both connection attempts. NAT configurations do not block this connection request.
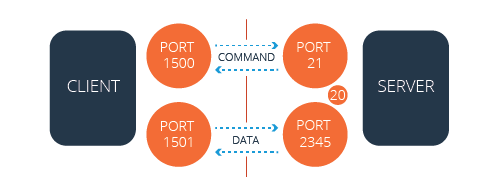
Passive FTP (with firewall)
The firewall does not block the server’s attempt to communicate with the client because the client initiated the communication both times.
The sections below explain how to edit the default configurations for a Pure-FTPd server and a ProFTPD server.
49152 through 65534 for Pure-FTPd servers and ProFTPD servers by default.To edit the FTP configuration for a PureFTP server, perform the following steps:
root user via SSH./var/cpanel/conf/pureftpd/local file, if it already exists, with a text editor. If it does not already exist, create the /var/cpanel/conf/pureftpd/local file.ForcePassiveIP option to the FTP server’s public IP address, as in the following example:
ForcePassiveIP: 203.0.113.0ForcePassiveIP option to the following entry:
ForcePassiveIP: ~ForcePassiveIP entry can exist in a configuration file.
|
|
/usr/local/cpanel/scripts/setupftpserver pure-ftpd --forceTo edit the FTP configuration for a ProFTPD server, perform the following steps:
root user via SSH./var/cpanel/conf/proftpd/local file, if it already exists, with a text editor. If it does not already exist, create the /var/cpanel/conf/proftpd/local file.MasqueradeAddress option to the FTP server’s public IP address, as in the following example:
MasqueradeAddress: 203.0.113.0MasqueradeAddress option to the following entry:
MasqueradeAddress: ~MasqueradeAddress entry can exist in a configuration file.
|
|
/usr/local/cpanel/scripts/setupftpserver proftpd --force49152 through 65534 for Pure-FTPd servers and ProFTPD servers by default.You may need to add your FTP server’s passive port range to the firewall manually.
If you use the ConfigServer Security & Firewall (CSF) plugin to manage your server’s firewall, open the /etc/csf/csf.conf file, and confirm that the passive port range exists at the end of the TCP_IN line. The system adds your FTP server’s passive port range to the firewall by default. For more information about how to install and use CSF, visit the CSF website.
If you use the nftables framework for your CentOS 8, AlmaLinux 8, or CloudLinux 8 server, run the following commands to add the passive port range to your server’s firewall:
|
|
You will find the nftables ruleset for your server in the /etc/sysconfig/nftables.conf file.
cPanel & WHM version 92 for CentOS 8 and CloudLinux 8 is experimental software and is not recommended for production environments. For more information, read our cPanel & WHM version 92 for CentOS 8 documentation.
Upgrade to a later version of cPanel & WHM to use CentOS 8 and CloudLinux 8 in production environments.
If you use the firewalld application for your CentOS 7, CloudLinux™ 7, or Red Hat® Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 server, run the following commands to add the passive port range to your server’s firewall:
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 deprecated the iptables utility. While cPanel, L.L.C. does not support this version of RHEL, this change affects all cPanel-supported operating systems. We recommend the nftables utility for servers that run CentOS 8, AlmaLinux 8, or CloudLinux 8. For servers that run CentOS 7, CloudLinux 7, or RHEL 7, we recommend that you use the firewalld utility.
cPanel & WHM version 92 for CentOS 8 and CloudLinux 8 is experimental software and is not recommended for production environments. For more information, read our cPanel & WHM version 92 for CentOS 8 documentation.
Upgrade to a later version of cPanel & WHM to use CentOS 8 and CloudLinux 8 in production environments.
For more information, read Red Hat’s When to use firewalld, nftables, or iptables documentation.
If you use the iptables application for your FTP server’s firewall, perform the following steps to add the passive port range to your server’s firewall:
iptables-services package if it does not already exist on your server. This package provides the iptables and ip6tables services, which are not included in the iptables application. To install this package, run the following command:
yum install iptables-services
|
|
If you use SolusVM and Xen® on a CloudLinux™ server, you may experience problems with Passive FTP. These problems may resemble a firewall or other connection issue, even when no firewall exists.
To resolve these issues, perform the following steps:
IPTABLES_MODULES= ip_conntrack_netbios_ns line in the /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config file on the VPS node with the following line:
IPTABLES_MODULES=ipt_REJECT ipt_tos ipt_TOS ipt_LOG ip_conntrack ipt_limit ipt_multiport iptable_filter iptable_mangle ipt_TCPMSS ipt_tcpmss ipt_ttl ipt_length ipt_state iptable_nat ip_nat_ftp ipt_owner ipt_REDIRECTservice iptables restart command to restart the iptables service.If your NAT-configured server cannot execute Passive FTP connections to other IP addresses on the server, perform either of the following actions:
ForcePassiveIP option with a tilde (~) character. The system interprets this character as an undefined directive and prevents automatic changes to the /etc/pure-ftpd.conf or /etc/proftpd.conf files.